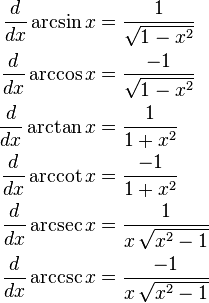The general formulas for diferentiating trigonometric functions are:
Example 1: Find the derivative of the folloiwing function.
a) f(x) = sin(3x^2 + 6x -5)
f `(x) = (6x + 6) cos(3x^2 + 6x -5)
f `(x) = 6 (x + 1) cos(3x^2 + 6x -5)
b) f(x) = sec(lnx)
f `(x) = sec(lnx) * tan(lnx) * (1/x)
f `(x) = sec(lnx)tan(lnx)
x
c) f(x) = cot(sinx)
f `(x) = - (csc(sinx))^2 * cosx
d) f(x) = (cos(sin3x))^2
f `(x) = 2*cos(sin3x)*sin(sin3x)*cos(3x)*3
f `(x) = 6*cos(sin3x)*sin(sin3x)*cos(3x)
NOTE: The chain rule was also used in this problem. If you are unfamiliar with the chain rule, click the image of the trigonometric functions. If not, a video is supplied.
For extra problems and practice, click here.